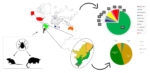
Review of tick species in two small synanthropic mammals, Didelphis albiventris (Lund, 1840) and Rattus rattus (Linnaeus, 1758)
Talita Oliveira, Renata Silva, Arthur Queiros, Thiara Guimarães, Kauane Freitas, Sofia Oliveira, Cecilia CalabuigThe present study aims to make a literature review, for the years between 1960 and 2022, of tick species that affect two species of small synanthropic mammals. A scientific literature review was carried out on the ticks that affect the species Didelphis albiventris (Lund, 1840) and Rattus rattus (Linnaeus, 1758), covering the years 1960 to 2022. The main countries that contributed to studies on the subject were: Brazil (N = 48), corresponding to 84% of the articles found, then Argentina, Angola, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, Australia, Italy, Singapore, the United States, and Taiwan, each contributing with one article (N = 1), representing 2% each of the articles found, totaling 16% remaining. We also observed differences between the percentages of studies on the small mammal species surveyed, with 77% carried out with the species D. albiventris, and 23% referring to R. rattus. Considering only the studies carried out in Brazil, which corresponded to 84%, Atlantic Forest and Cerrado seem to be the biomes with the most published studies, with ticks for both host species (N = 34) 47% and (N = 30) 42%, respectively. 7% (N = 5) of the studies were found for the Caatinga biome and 4% (N = 3) for the Pampa biome.
Espécies de carrapatos em dois pequenos mamíferos sinantrópicos. O presente estudo tem como objetivo fazer uma revisão de literatura, para os anos de 1960 a 2022, das espécies de carrapatos que acometem duas espécies de pequenos mamíferos sinantrópicos. Foi realizada revisão da literatura científica sobre os carrapatos que acometem as espécies Didelphis albiventris (Lund, 1840) e Rattus rattus (Linnaeus, 1758), abrangendo os anos de 1960 a 2022. Os principais países que contribuíram com estudos sobre o tema foram: Brasil (N = 48), correspondendo a 84% dos artigos encontrados; depois por Argentina, Angola, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, Austrália, Itália, Cingapura, Estados Unidos e Taiwan, cada um contribuindo com um artigo (N = 1), representando 2% cada um dos artigos encontrados, totalizando 16% restantes. Também observamos diferenças entre os percentuais de estudos sobre as espécies de pequenos mamíferos pesquisadas, com 77% realizados com a espécie D. albiventris, e 23% referentes a R. rattus. Considerando apenas os estudos realizados no Brasil, que corresponderam a 84%, Mata Atlântica e Cerrado parecem ser os biomas com mais estudos publicados, com carrapatos para ambas as espécies hospedeiras (N = 34) 47% e (N = 30) 42%, respectivamente. 7% (N = 5) dos estudos foram encontrados para o bioma Caatinga e 4% (N = 3) para o bioma Pampa.